class URLSessionclass URLSessionTask Technology
For small interactions with remote servers, you can use the URLSession class to receive response data into memory (as opposed to using the URLSession class, which stores the data directly to the file system). A data task is ideal for uses like calling a web service endpoint.
リモートサーバーとの少しの相互作用に対して、あなたはURLSessionクラスを使って、応答データをメモリに受け取ることができます(URLSessionクラスを使うこととはまったく異なります、それはデータを直接にファイルシステムに格納します)。データタスクは、ウェブサービスエンドポイントを呼び出すことのような用法に最適です。
You use a URL session instance to create the task. If your needs are fairly simple, you can use the shared instance of the URLSession class. If you want to interact with the transfer through delegate callbacks, you’ll need to create a session instead of using the shared instance. You use a URLSession instance when creating a session, also passing in a class that implements URLSession or one of its subprotocols. Sessions can be reused to create multiple tasks, so for each unique configuration you need, create a session and store it as a property.
あなたは、URLセッションインスタンスを使ってタスクを作成します。あなたの要求がまあまあ単純ならば、あなたはURLSessionクラスのsharedインスタンスを使用できます。あなたが委任先コールバックを通してその転送と相互作用したいならば、あなたは共有インスタンスを使う代わりにセッションを作成する必要があるでしょう。あなたは、セッションを作成する場合にURLSessionインスタンスを使います、そしてURLSessionまたはそれのサブプロトコルの1つを実装するあるクラスに渡します。セッションは複数のタスクを作成するために再利用できます、それゆえあなたが必要とする固有の構成設定それぞれに対して、あるセッションを作成してそれをプロパティとして格納してください。
Note 注意
Be careful to not create more sessions than you need. For example, if you have several parts of your app that need a similarly configured session, create one session and share it among them. あなたが必要とするより多くのセッションを作成しないよう気をつけてください。例えば、あなたがある同様に構成設定されたセッションを必要とするあなたのアプリの幾つかの部分を持つならば、1つのセッションを作成してそれをそれらの間で共有してください。
Once you have a session, you create a data task with one of the data methods. Tasks are created in a suspended state, and can be started by calling resume().
一旦あなたがあるセッションを持つならば、あなたはデータタスクをdataメソッドそれらのうちの1つで作成します。タスクは、ある一時停止状態で作成されます、そしてresume()を呼び出すことによって開始できます。
The simplest way to fetch data is to create a data task that uses a completion handler. With this arrangement, the task delivers the server’s response, data, and possibly errors to a completion handler block that you provide. Figure 1 shows the relationship between a session and a task, and how results are delivered to the completion handler. データを取って来る最も単純な方法は、完了ハンドラを使うデータタスクを作成することです。この解決で、タスクはサーバーのもつ応答、データ、そしてことによるとエラーを、あなたが提供する完了ハンドラブロックに配達します。図 1 は、セッションとタスクの間の関係、そしてどのように結果が完了ハンドラに配達されるかを示します。

To create a data task that uses a completion handler, call the data method of URLSession. Your completion handler needs to do three things:
完了ハンドラを使うデータタスクを作成するには、URLSessionのdataメソッドを呼び出してください。あなたの完了ハンドラは、3つのことをする必要があります:
Verify that the error parameter is nil. If not, a transport error has occurred; handle the error and exit.
errorパラメータがnilであることを検証してください。そうでないならば、転送エラーが発生しています;そのエラーを処理して退出してください。
Check the response parameter to verify that the status code indicates success and that the MIME type is an expected value. If not, handle the server error and exit.
responseパラメータを調べて、状態コードが成功を指し示すことそしてMIMEタイプが予想される値であることを検証してください。そうでないならば、サーバーエラーを処理して退出してください。
Use the data instance as needed.
dataインスタンスを必要に応じて使用してください。
Listing 1 shows a start method for fetching a URL’s contents. It starts by using the URLSession class’s shared instance to create a data task that delivers its results to a completion handler. After checking for local and server errors, this handler converts the data to a string, and uses it to populate a WKWeb outlet. Of course, your app might have other uses for fetched data, like parsing it into a data model.
それはURLSessionクラスのもつ共有インスタンスを使うことでそれの結果を完了ハンドラに配達するあるデータタスクを作成することによって始めます。ローカルおよびサーバーエラーを調べた後、このハンドラはそのデータを文字列に変換します、そしてそれを使ってWKWebアウトレットを満たします。もちろん、あなたのアプリは、取って来たデータに他の使い方をするかもしれません、それをあるデータモデルへと構文解析することのような。
func startLoad() {
let url = URL(string: "https://www.example.com/")!
let task = URLSession.shared.dataTask(with: url) { data, response, error in
if let error = error {
self.handleClientError(error)
return
}
guard let httpResponse = response as? HTTPURLResponse,
(200...299).contains(httpResponse.statusCode) else {
self.handleServerError(response)
return
}
if let mimeType = httpResponse.mimeType, mimeType == "text/html",
let data = data,
let string = String(data: data, encoding: .utf8) {
DispatchQueue.main.async {
self.webView.loadHTMLString(string, baseURL: url)
}
}
}
task.resume()
}
Important 重要
The completion handler is called on a different Grand Central Dispatch queue than the one that created the task. Therefore, any work that uses data or error to update the UI — like updating web — should be explicitly placed on the main queue, as shown here.
完了ハンドラは、タスクが作成されたものと異なるグランドセントラルディスパッチキュー上で呼び出されます。したがって、dataまたはerrorを使ってUIを更新するあらゆる仕事 — webを更新することのような — は、明示的にメインキュー上に置かれるべきです、ここで示されるように。
For a greater level of access to the task’s activity as it proceeds, when creating the data task, you can set a delegate on the session, rather than providing a completion handler. Figure 2 shows this arrangement. タスクの活動へのそれが進むにつれてのより重要な水準のアクセスに対して、データタスクを作成している時に、あなたは委任先をそのセッション上で設定できます、完了ハンドラを提供するのではなく。図 2 は、この手はずを示します。
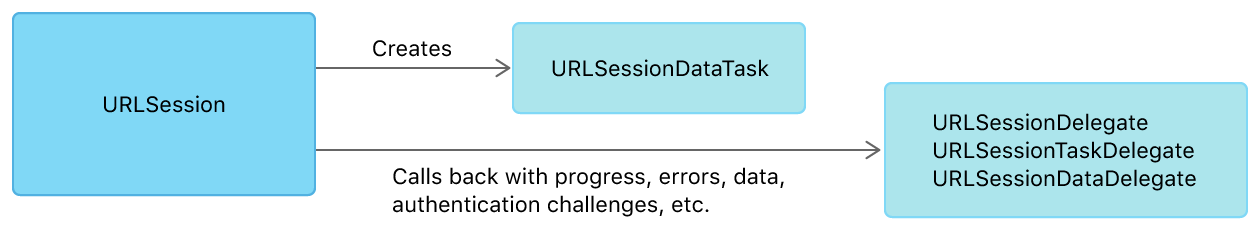
With this approach, portions of the data are provided to the url method of URLSession as they arrive, until the transfer finishes or fails with an error. The delegate also receives other kinds of events as the transfer proceeds.
この取り組みでは、データの部分それらはURLSessionのurlメソッドにそれらが到着するにつれて提供されます、転送が終了するかエラーで失敗するまで。委任先はまた、他の種類のイベントを転送が進むにつれて受け取ります。
You need to create your own URLSession instance when using the delegate approach, rather than using the URLSession class’s simple shared instance. Creating a new session allows you to set your own class as the session’s delegate, as shown in Listing 2.
あなたは、あなた独自のURLSessionインスタンスを作成する必要があります、URLSessionクラスのもつ単純なsharedインスタンスを使っているのではなく、委任先手法を使っている時は。新しいセッションを作成することは、あなたにあなた独自のクラスをそのセッションのもつ委任先として設定させます、コード出力 2において示されるように。
Declare that your class implements one or more of the delegate protocols (URLSession, URLSession, URLSession, and URLSession). Then create the URL session instance with the initializer init(configuration:. You can customize the configuration instance used with this initializer. For example, it’s a good idea to set waits to true. That way, the session waits for suitable connectivity, rather than failing immediately if the required connectivity is unavailable.
あなたのクラスが1つ以上の委任先プロトコルを実装することを宣言してください(URLSession、URLSession, URLSession、そしてURLSession)。それからURLセッションインスタンスをイニシャライザinit(configuration:で作成してください。あなたは、構成設定インスタンスをこのイニシャライザでカスタマイズできます。例えば、waitsをtrueに設定することは良い考えです。そのようにして、セッションは適切な接続性に対して待機します、要求される接続性が利用可能でないならばすぐに失敗するのではなく。
private lazy var session: URLSession = {
let configuration = URLSessionConfiguration.default
configuration.waitsForConnectivity = true
return URLSession(configuration: configuration,
delegate: self, delegateQueue: nil)
}()
Listing 3 shows a start method that uses this session to start a data task, and uses delegate callbacks to handle received data and errors. This listing implements three delegate callbacks:
コード出力 3 は、あるstartメソッドを示します、それはこのセッションを使ってデータタスクを開始します、そして委任先コールバックを使って受信されたデータとエラーを取り扱います。このコード出力は、3つの委任先コールバックを実装します:
url verifies that the response has a succesful HTTP status code, and that the MIME type is text/html or text/plain. If either of these is not the case, the task is canceled; otherwise, it’s allowed to proceed.
urlは、応答が成功HTTP状態コードを持つこと、そしてMIME型がtext/htmlまたはtext/plainであることを検証します。どちらかが事実でないならば、タスクは取り消されます;そうでなければ、それは処理を許可されます。
url takes each Data instance received by the task and appends it to a buffer called received.
urlは、タスクによって受け取られるDataインスタンスそれぞれを取り、そしてそれをreceivedと呼ばれるパッファに追加します。
url first looks to see if a transport-level error has occurred. If there is no error, it attempts to convert the received buffer to a string and set it as the contents of web.
urlは、まず転送レベルエラーが起こったかどうか知るために確かめます。エラーがないならば、それはreceivedバッファを文字列へと変換してそれをwebの内容として設定しようと試みます。
var receivedData: Data?
func startLoad() {
loadButton.isEnabled = false
let url = URL(string: "https://www.example.com/")!
receivedData = Data()
let task = session.dataTask(with: url)
task.resume()
}
// delegate methods
func urlSession(_ session: URLSession, dataTask: URLSessionDataTask, didReceive response: URLResponse,
completionHandler: @escaping (URLSession.ResponseDisposition) -> Void) {
guard let response = response as? HTTPURLResponse,
(200...299).contains(response.statusCode),
let mimeType = response.mimeType,
mimeType == "text/html" else {
completionHandler(.cancel)
return
}
completionHandler(.allow)
}
func urlSession(_ session: URLSession, dataTask: URLSessionDataTask, didReceive data: Data) {
self.receivedData?.append(data)
}
func urlSession(_ session: URLSession, task: URLSessionTask, didCompleteWithError error: Error?) {
DispatchQueue.main.async {
self.loadButton.isEnabled = true
if let error = error {
handleClientError(error)
} else if let receivedData = self.receivedData,
let string = String(data: receivedData, encoding: .utf8) {
self.webView.loadHTMLString(string, baseURL: task.currentRequest?.url)
}
}
}The various delegate protocols offer methods beyond those shown in the above code, for handling authentication challenges, following redirects, and other special cases. Using a URL Session, in the URLSession discussion, describes the various callbacks that may occur during a transfer.
さまざまな委任先プロトコルは、上のコードにおいて示されるそれらを越えるメソッドを提案して、リダイレクト、そして他の特殊事例を取り扱っています。Using a URL Sessionは、URLSessionの議論において、転送の間に起こるかもしれないさまざまなコールバックを記述します。
class URLSessionclass URLSessionTask