Overview 概要
When your app makes a request with a NSURLSession, the server may respond with one or more demands for credentials before continuing. The session task attempts to handle this for you. If it can’t, it calls your session’s delegate to handle the challenges.
あなたのアプリがある要請をNSURLSessionでする場合、サーバーは続ける前に1つ以上の資格情報の要求で応答するかもしれません。セッションタスクは、これをあなたのために取り扱います。それができないならば、それはあなたのセッションのもつdelegateを呼び出してそのチャレンジを取り扱います。
Implement the delegate methods described in this article to answer challenges issued by a server that your app connects to. If you don’t implement a delegate, your request may be denied by the server, and you receive a response with HTTP status code 401 (Forbidden) instead of the data you expect.
この記事で記述される委任先メソッドを実装して、あなたのアプリが接続するところのサーバーによって出されるチャレンジに答えてください。あなたが委任先を実装しないならば、あなたのリクエストはサーバーによって拒絶されるでしょう、そしてあなたは応答をHTTP状態コード401 (Forbidden) で受け取るでしょう、あなたが期待するデータではなしに。
Determine the Appropriate Delegate Method 適切な委任先メソッドを決定する
Implement one or both delegate authentication methods, depending on the nature of the challenge(s) you receive. 1つまたは両方の委任先認証メソッドを実装してください、あなたが受け取るそのチャレンジ(または複数)に基づいて。
Implement the
URLSession:method ofdid Receive Challenge: completion Handler: NSURLSessionto handle session-wide challenges. These are challenges like Transport Layer Security (TLS) validation. Once you’ve successfully handled this kind of challenge, your action remains in effect for all tasks created from thatDelegate NSURLSession.NSURLSessionのDelegate URLSession:メソッドを実装して、セッション単位のチャレンジを取り扱ってください。Transport Layer Security(TLS)検証のようなチャレンジがあります。一旦あなたが成功裏にこの種のチャレンジを処理するならば、あなたのアクションはそのdid Receive Challenge: completion Handler: NSURLSessionから作成された全てのタスクに対して有効なままです。Implement the
URLSession:method oftask: did Receive Challenge: completion Handler: NSURLSessionto handle task-specific challenges. These are challenges like demands for username/password authentication. Each task created from a given session may issue its own challenges.Task Delegate NSURLSessionのTask Delegate URLSession:メソッドを実装して、タスク特有のチャレンジを取り扱ってください。ユーザ名/パスワード認証の要求のようなチャレンジがあります。ある与えられたセッションから作成された各タスクは、それ自身のチャレンジを発行するかもしれません。task: did Receive Challenge: completion Handler:
Note 注意
See NSURLProtectionSpace Authentication Method Constants for a guide to which authentication methods are session-wide or task-specific. NSURLProtectionSpace認証メソッド定数をどの認証メソッドがセッション単位またはタスク特有であるかに対するガイドとして見てください。
As a simple example, consider what happens when you request an http URL protected by HTTP Basic authentication, as defined in RFC 7617. Because this is a task-specific challenge, you handle this by implementing URLSession:.
単純な例として、RFC 7617で定義されるようにHTTP Basic認証によって保護されたhttp URLをあなたがリクエストする時に何が起こるか考えてください。これがタスク特有のチャレンジであることから、あなたはこれをURLSession:を実装することによって取り扱います。
Note 注意
If you connect via https, you also receive a server trust challenge. See Performing Manual Server Trust Authentication for information on handling this type of session-wide challenge.
あなたがhttpsによって接続するならば、あなたはまたサーバー信用チャレンジを受け取ります。手動でサーバー信用認証を実行するをこの型のセッション単位のチャレンジを取り扱う上での情報として見てください。
Figure 1 outlines a strategy for responding to the HTTP Basic challenge. 図 1 は、HTTP Basicチャレンジに応答するための方策の要点を述べます。
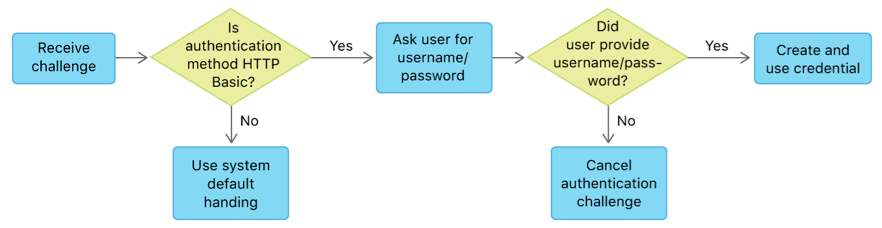
The following sections implement this strategy. 後の続く節は、この方策を実装します。
Determine the Type of Authentication Challenge 認証チャレンジの型を決定する
When you receive an authentication challenge, use your delegate method to determine the type of challenge. The delegate method receives a NSURLAuthentication instance that describes the challenge being issued. This instance contains a protection property whose authentication property indicates the kind of challenge being issued (such as a request for a username and password, or a client certificate). You use this value to determine whether you can handle the challenge.
あなたがある認証チャレンジを受け取る時、あなたの委任先メソッドを使ってチャレンジの型を決定してください。委任先メソッドは、あるNSURLAuthenticationインスタンスを受け取ります、それは発行されているチャレンジを記述します。このインスタンスは、protectionプロパティを含みます、それのauthenticationプロパティは発行されているチャレンジの種類を指し示します(たとえばユーザ名とパスワードの要求、またはクライアント証明書など)。あなたは、この値を使ってあなたがそのチャレンジを取り扱えるかどうかを決定します。
You respond to the challenge by directly invoking the completion handler passed in to the challenge, passing an NSURLSession indicating your response to the challenge. You use the disposition argument to provide a credential, cancel the request, or allow the default handling to proceed, whichever is appropriate.
あなたは、チャレンジに渡される完了ハンドラを、チャレンジに対するあなたの応答を指し示しているNSURLSessionを渡して、直接に発動することによってチャレンジに応答します。あなたは、意向の引数を使うことで、資格情報を提供する、リクエストを取り消す、または省略時の処理に続けさせる、どれでも適切なことをします。
Listing 1 tests the authentication method to see if it is the expected type, HTTP Basic. If the authentication property indicates some other kind of challenge, it calls the completion handler with the NSURLSession disposition. Telling the task to use its default handling may satisfy the challenge; otherwise, the task will move on to the next challenge in the response and call this delegate again. This process continues until the task reaches the HTTP Basic challenge that you expect to handle.
コード出力 1 は、認証メソッドをテストして、それが期待する型、HTTP Basicであるかを見ます。authenticationプロパティが何か他の種類のチャレンジを指し示すならば、それは完了ハンドラをNSURLSessionの意向で呼び出します。それの省略時の処理を使うようにタスクに伝えることは、そのチャレンジを満足させるかもしれません;そうでなければ、タスクはその応答において次のチャレンジへと移動します、そしてこの委任先を再び呼び出すでしょう。この過程は、あなたが取り扱うのを期待するHTTP Basicチャレンジに、そのタスクが到達するまで続きます。
let authMethod = challenge.protectionSpace.authenticationMethod
guard authMethod == NSURLAuthenticationMethodHTTPBasic else {
completionHandler(.performDefaultHandling, nil)
return
}Create a Credential Instance 資格情報インスタンスを作成する
To successfully answer the challenge, you need to submit a credential appropriate to type of challenge you have received. For HTTP Basic and HTTP Digest challenges, you provide a username and password. Listing 2 shows a helper method that attempts to create a NSURLCredential instance from user-interface fields, if they are filled in.
成功裏にチャレンジに応えるには、あなたは、あなたが受け取ったチャレンジの型に適切な資格情報を提出する必要があります。HTTP Basic と HTTP Digest チャレンジに対して、あなたはユーザ名とパスワードを提供します。コード出力 2 は、あるヘルパーメソッドです、それはNSURLCredentialインスタンスをユーザインターフェイスの各欄から作成します、もしそれらが記入されるならば。
func credentialsFromUI() -> URLCredential? {
guard let username = usernameField.text, !username.isEmpty,
let password = passwordField.text, !password.isEmpty else {
return nil
}
return URLCredential(user: username, password: password,
persistence: .forSession)
}In this example, the returned NSURLCredential has NSURLCredential persistence, so it’s only stored by the NSURLSession instance that created the task. You would need to supply new NSURLCredential instances for tasks created by other session instances, and on future runs of the app.
この例では、返されるNSURLCredentialは、NSURLCredential永続性を持ちます、なのでそれはそのタスクによって作成されたNSURLSessionインスタンスによって格納されるだけです。あなたは、新しいNSURLCredentialインスタンスを他のセッションインスタンスによって作成されたタスクに対して、そしてそのアプリの将来の実行に関して、供給する必要があるでしょう
Call the Completion Handler 完了ハンドラを呼び出す
Once you’ve tried to create a credential instance, you must call the completion handler to answer the challenge. 一旦あなたが資格情報インスタンスを作成する試みをしたならば、あなたは完了ハンドラを呼び出してチャレンジに答えなければなりません。
If you can’t create a credential, or if the user explicitly canceled, call the completion handler and pass the
NSURLSessiondisposition. あなたがある資格情報を作成できないならば、またはユーザが明示的に取り消したならば、完了ハンドラを呼び出してAuth Challenge Cancel Authentication Challenge NSURLSessionの意向を渡してください。Auth Challenge Cancel Authentication Challenge If you can create a credential instance, use the
NSURLSessiondisposition to pass it to the completion handler. あなたが資格情報インスタンスを作成できるならば、Auth Challenge Use Credential NSURLSessionの意向を使ってそれを完了ハンドラに渡してください。Auth Challenge Use Credential
Listing 3 shows both these options. コード出力 3 は、それらオプションの両方を示します。
guard let credential = credentialOrNil else {
completionHandler(.cancelAuthenticationChallenge, nil)
return
}
completionHandler(.useCredential, credential)If you supply a credential that is accepted by the server, the task begins uploading or downloading data. あなたがサーバによって受け入れられる資格情報を供給するならば、タスクはデータのアップロードまたはダウンロードを開始します。
Important 重要
You can pass the completion handler to other methods or temporarily store it in a property, for situations like waiting for the user to complete a username/password dialog. But eventually you must call the completion handler to complete the challenge and allow the task to proceed, even if you’re choosing to cancel, as seen in the failure case of Listing 3. あなたは、完了ハンドラを他のメソッドに渡すことまたは一時的にそれをあるプロパティの中に格納することができます、ユーザがユーザ名/パスワードのダイアログを完成させるのを待っているような状況に対しては。しかし最後にはあなたは完了ハンドラを呼び出してチャレンジを完了してそしてタスクが続行できるようにしなければなりません、たとえあなたがキャンセルを選んでいるとしてもです、コード出力 3 の失敗の場合において見られるように。
Handle Failures Gracefully 失敗を優雅に取り扱う
If the credential is refused, the system calls your delegate method again. When this happens, the callback provides your rejected credential as the proposed property of the NSURLAuthentication parameter. The challenge instance also includes a previous property, which indicates how many times the credential has been rejected. You can use these properties to determine what to do next. For example, if the previous is greater than zero, you could use the user string of the proposed to populate a user/password reentry UI.
資格情報が拒絶されるならば、システムはあなたの委任先メソッドを再び呼び出します。これが起こる場合、コールバックはあなたの拒絶された資格情報をNSURLAuthenticationパラメータのproposedプロパティとして提供します。チャレンジインスタンスはまた、previousプロパティを含みます、それはどれくらい多くの回数その資格情報が拒絶されたかを指し示します。あなたは、それらプロパティを使って次に何をするか決定します。例えば、previousがゼロより大きいならば、あなたはproposedのユーザ文字列を使って、ユーザ/パスワード再記入UIを満たすことができます。