struct LazyHStack struct LazyVStack struct PinnedScrollableViews Technology
Lazy and Lazy views are both able to display groups of views organized into logical sections, arranging their children in lines that grow horizontally and vertically, respectively. These stacks are “lazy” in that the stack views don’t create items until they need to be rendered onscreen. Like stack views, lazy stacks don’t include any inherent support for scrolling, and you should wrap lazy stack views in Scroll containers.
To group content or data inside a lazy stack view, use Section instances as containers for collections of grouped views. Section views don’t have any visual representation themselves but can contain header and footer views that can either scroll with the stack’s content or that you can pin to the top or bottom of the Scroll.
Note 注意
Use Section views to get platform-appropriate grouping inside stack views or lazy stacks, lazy grids, List, Command, Form, and several other container types.
The code samples in this article build a user interface for visualizing shades of primary colors. Each section in the stack represents a primary color, containing five subviews, each showing a different variation of the color.
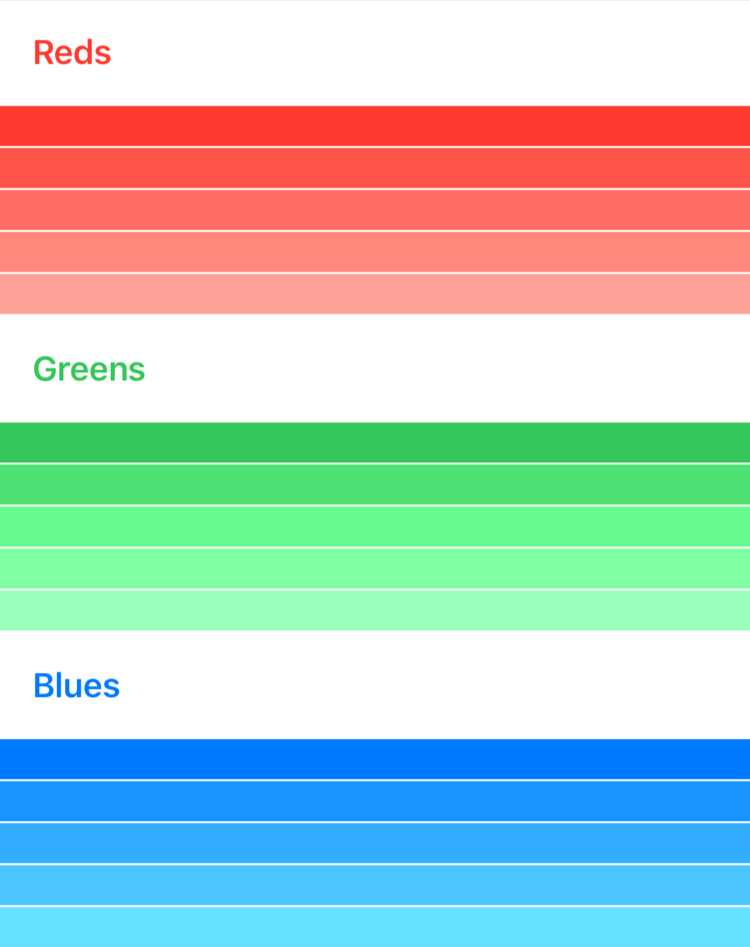
As with views contained within a stack, each Section must be uniquely identifiable when iterated by For. In this example, Color instances represent the sections, and Shade instances represent the shades of each color inside a section. Both Color and Shade conform to the Identifiable protocol.
struct ColorData: Identifiable {
let id = UUID()
let name: String
let color: Color
let variations: [ShadeData]
struct ShadeData: Identifiable {
let id = UUID()
var brightness: Double
}
init(color: Color, name: String) {
self.name = name
self.color = color
self.variations = stride(from: 0.0, to: 0.5, by: 0.1)
.map { ShadeData(brightness: $0) }
}
}The Color below sets up an array containing Color instances for each primary color. The Lazy iterates over the array of color data to create sections, then iterates over the variations to create views from the shades.
struct ColorSelectionView: View {
let sections = [
ColorData(color: .red, name: "Reds"),
ColorData(color: .green, name: "Greens"),
ColorData(color: .blue, name: "Blues")
]
var body: some View {
ScrollView {
LazyVStack(spacing: 1) {
ForEach(sections) { section in
Section(header: SectionHeaderView(colorData: section)) {
ForEach(section.variations) { variation in
section.color
.brightness(variation.brightness)
.frame(height: 20)
}
}
}
}
}
}
}Group data with Section views and pass in a header or footer view with the header and footer properties. This example implements a Section as a header view, containing a semi-transparent stack view and the name of the section’s color in a Text label.
struct SectionHeaderView: View {
var colorData: ColorData
var body: some View {
HStack {
Text(colorData.name)
.font(.headline)
.foregroundColor(colorData.color)
Spacer()
}
.padding()
.background(Color.primary
.colorInvert()
.opacity(0.75))
}
}For more information on using For to repeat views inside a stack, see Creating Performant Scrollable Stacks.
By default, section header and footer views will scroll in sync with section content. If you want header and footer views to always remain visible, regardless of whether the top or bottom of the section is visible, then specify a set of Pinned for the pinned property of the lazy stack view.
LazyVStack(spacing: 1, pinnedViews: [.sectionHeaders]) {
// ...
}In Lazy containers, headers attach to the top and footers to the bottom. In Lazy containers, headers attach to the leading edge and footers to the trailing edge.
With this change, section headers are pinned to the top of the view as the user begins to scroll.

struct LazyHStack struct LazyVStack struct PinnedScrollableViews